
Learning Points
In this month's Clinical Skills article, best practice for the administration of intramuscular (IM) injections will be discussed. It is important to re-visit clinical skills as many are taught during initial training and then not re-visited. This can lead to poor practice and incorrect technique, which in turn can lead to patient discomfort and potential complications (Hunter, 2008; Malkin, 2008). An overview of injection sites, indications and complications will be provided with an evidence-based approach to best practice technique. Full critique of the injection sites will not be explored here owing to the overview nature of this article.
It is important for patient care to ensure optimal effects of the medications administered, and to minimise the experience of any discomfort or pain. Within paramedic practice, examples of medications administered via the IM route include:
Injection sites
There are five known sites identified for intramuscular injections with differences in the literature in terms of which are recommended (Thomas and Monaghan, 2014) (Figure 1):
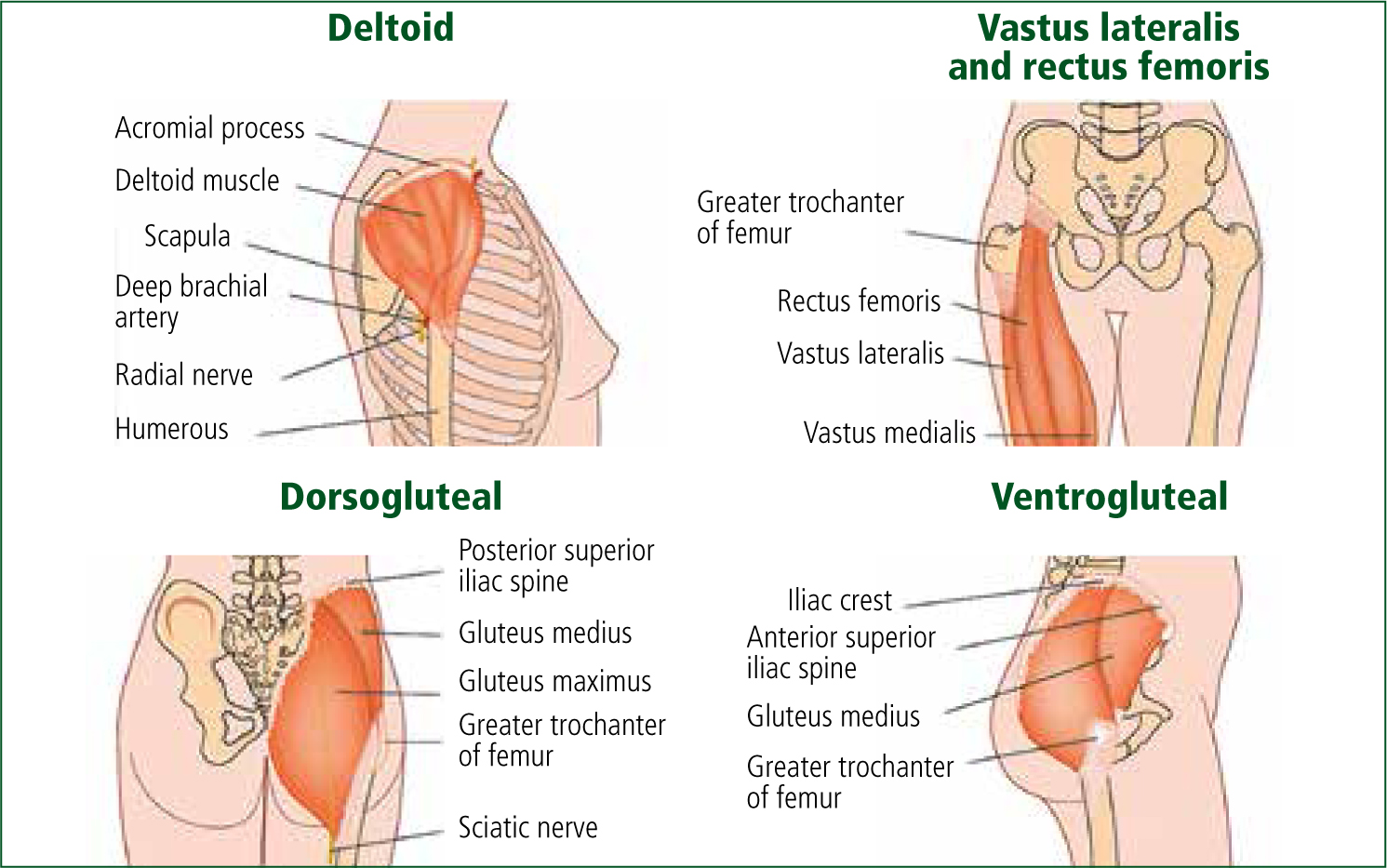
All sites have nerve innervation and blood supply; however only the dorsogluteal route is near to major blood vessels and nerves, and is therefore discouraged as a site for use (Ogston-Tuck, 2014). The Joint Royal Colleges Ambulance Liaison Committee (JRCALC) (2017) and Caroline (2014) primarily recommend the antero-lateral aspects of the thigh or upper arm for administration for their ease of access and rapid absorption. The ventrogluteal site is widely recommended for IM injection owing to the minimal risk of damage to nerves and blood vessels; however, clinicians report infrequent use of this site because of an unfamiliarity with landmarks and difficulty in ensuring optimal patient positioning for administration (Cocoman and Murray, 2006; Wynaden, 2014; Strohfus et al, 2018). For multiple injections, varied sites should be used.
Site landmarks
Deltoid
Locate the ‘nobbly’ acromium process at the tip of the shoulder and then move your fingers 2.5 cm down onto the deltoid muscle. The patient's arm should be placed relaxed across their waist. This site is easily accessible but is recommended only for a volume up to 1 ml (Rodger and King, 2000; Cocoman and Murray, 2006; Ogston-Tuck, 2014). The deltoid is the preferred site for older children (Anon, 2007; Ogston-Tuck, 2014).
Ventro-gluteal
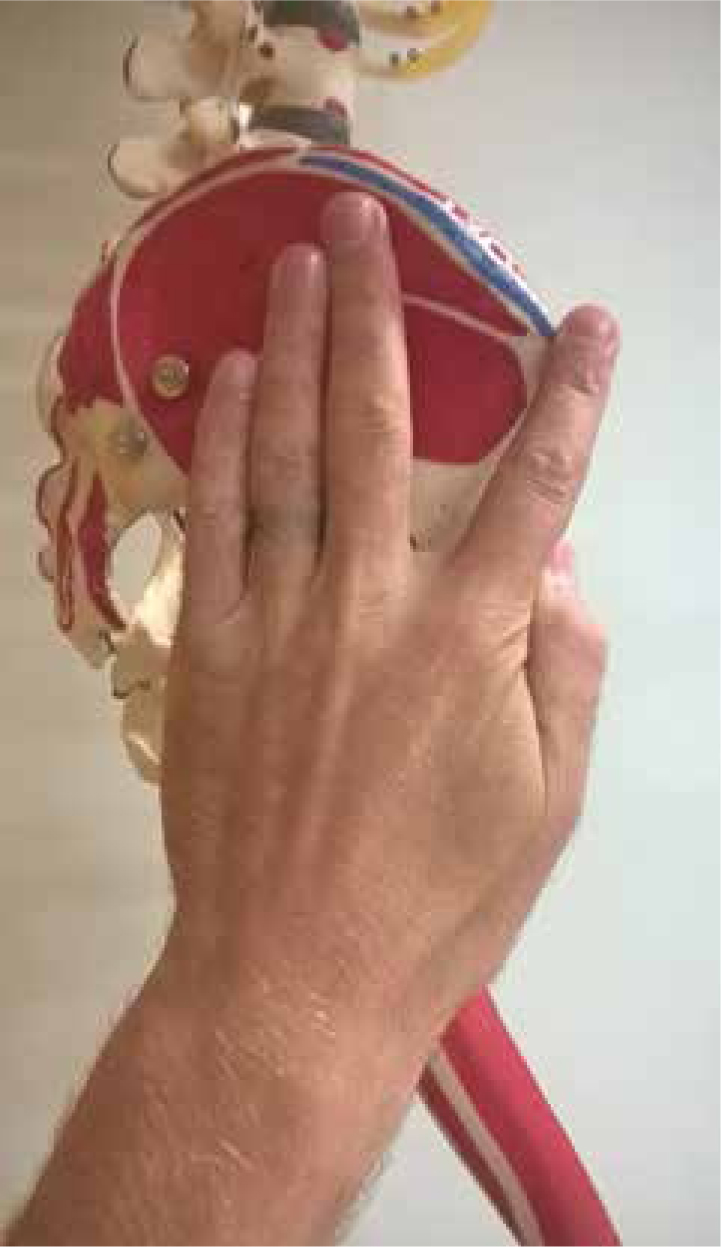
Place the heel of your hand on the patient's opposite hip (greater trochanter). For example, left hand on right hip. Make a V-shape with the first and second fingers, pointing the forefinger towards the iliac crest. The injection site is then located within this V in the gluteus medius muscle when the forefinger and second finger are splayed (Ogston-Tuck, 2014) (Figure 2). Up to 5 ml can be administered here (Rodger and King, 2000).

Rectus femoris
Located halfway between the patella and superior iliac crest on the anterior surface of the thigh (Hunter, 2008; Ogston-Tuck, 2014). Up to 5 ml can be administered in the rectus femoris.
Vastus lateralis
A hand's breadth from the greater trochanter and also the patella on the lateral surface of the thigh (Hunter, 2008; Ogston-Tuck, 2014). Up to 5 ml can be injected in the vastus lateralis (Rodger and King, 2000). It is an easy site to access (Floyd and Meyer, 2007), and is the preferred site for younger children and infants (Workman, 1999; Anon, 2007; Ogston-Tuck, 2014).
Site cleansing
The literature provides conflicting information regarding the cleansing of the injection site, with many hospital trusts recommending that if the skin is visibly clean, there is no requirement to use an alcohol-based cleansing wipe (Hunter, 2008). With correct use of aseptic technique, clean hands and gloves, injections can be administered without the requirement to clean the site. Conversely, some authors advise use of a 70% isopropyl-alcohol-based wipe to clean the site for 30 seconds, and then allowing to dry for 30 seconds (Hunter, 2008; Ogston-Tuck, 2014). In this case, it is important to allow the site to fully dry, as injecting in a still-wet site could increase the risk of pain experienced and bacteria entering the site of insertion (Workman, 1999). For patients who are immunocompromised, skin disinfection is recommended (Ogston-Tuck, 2014). Clinicians should therefore follow guidance and policy provided at local level with regards to site preparation/cleansing.
Clinical Indications
Indications for IM injection
Indications for individual medications will necessitate when an IM injection is required. The IM route is used for medications needing rapid absorption (10–20 minutes) but prolonged duration of action (Ogston-Tuck, 2014). Drug volumes of 1–5 ml can be administered via the IM route (Workman, 1999). In certain instances, such as for hypoglycaemic patients, intravenous (IV) administration of Glucose 10% is preferred ahead of IM Glucagon; however, clinical and situational factors need to be considered prior to making the clinical decision.
Contraindications
Injection sites where oedema, inflammation, infection or skin lesions and poor perfusion are present should be avoided. The site must be well-perfused to ensure absorption of the medication into the muscle (Caroline, 2014; Thomas and Monaghan, 2014).
Performing the procedure
Conclusion
Intramuscular injections form part of the skill set for paramedics and it is important to regularly re-visit clinical skills to ensure best practice is followed. Clinical and environmental factors, along with individual patient requirements, will impact the chosen site and delivery of IM injection. Paramedics need to maintain the required underpinning knowledge of their skills to provide best practice and quality patient care.

